|
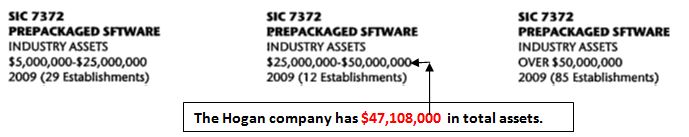
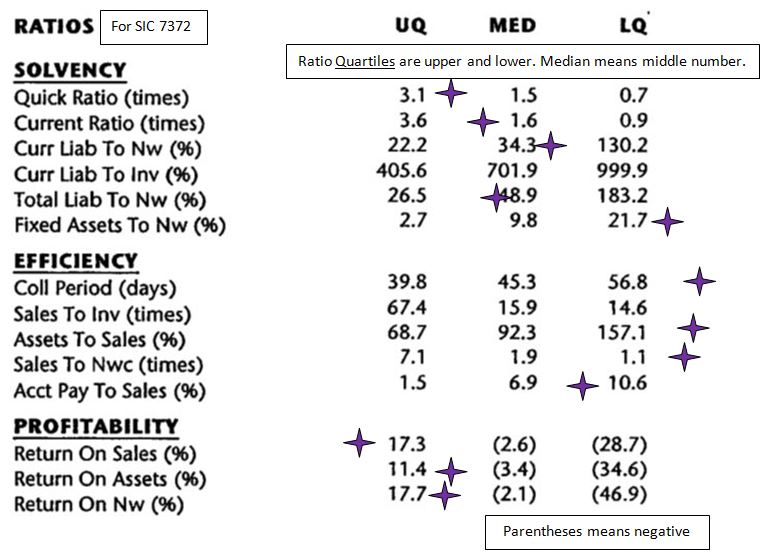
First, we need to find out what are the assets of the prospective company. The Hogan company has $47,108,000 in total assets. Second, we need to obtain the SIC code for the company. SIC code is 7372. Third, we need to go to the proper page in the D&B reference book. Sample of headings of pages is shown below. |